There are two types of devices participating in the protocol – brokers and clients. Brokers are the devices which host and relays data. Clients are the devices which access and modify data by publishing topics and receive other devices’ topics by subscribing. Let us take an example of the bulletin board. On the notice board, you might go through the topics which you have interest in. If you have something interesting to put up on the notice board, you are free to do that. To get the attention of the people who are interested in the topic, it is usually done in big bold letters. This is exactly how MQTT works.
Quality of Service (QoS)
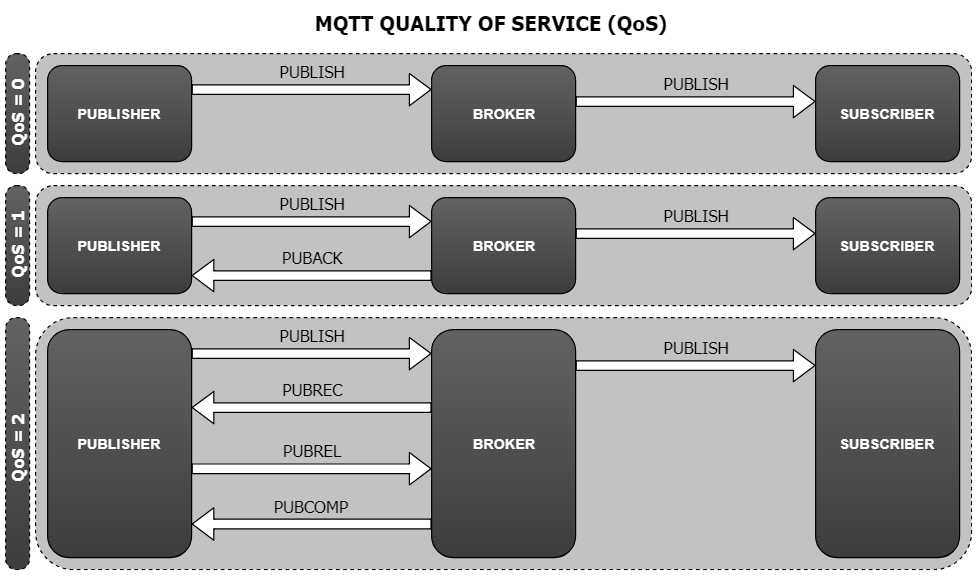
The MQTT also gives a provision for three Quality of Service (QoS) – 0, 1 and 2.
MQTT QoS
For QoS = 0, it ensures at most one delivery of the topic. It is equivalent to a ‘fire and forget’ concept.
For QoS = 1, it ensures at least one delivery of the topic. It receives an acknowledgment. It makes sure that the broker has received the message.
For QoS = 2, it ensures exactly one delivery of the topic. It gives us an assurance to the delivery of the message.
Không có nhận xét nào:
Đăng nhận xét